When Output Increases The Ppc Of The Economy?
Have you ever wondered how the production output affects the economy? Well, in this article, we’ll explore the fascinating topic of when output increases the PPC (Production Possibility Curve) of an economy.
When a country produces more goods and services, it can experience significant changes in its PPC.
But what exactly is the PPC, and how does it relate to the output of an economy? Let’s dive in and find out!
When Output Increases the Ppc of the Economy: Unlocking Economic Growth
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of how output increases the Ppc (Production Possibility Curve) of the economy and its impact on economic growth. In this article, we will delve into the concept of the Ppc, discuss the various factors that lead to an increase in output, and examine the effects it has on the overall health and prosperity of an economy. So let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of economic growth!
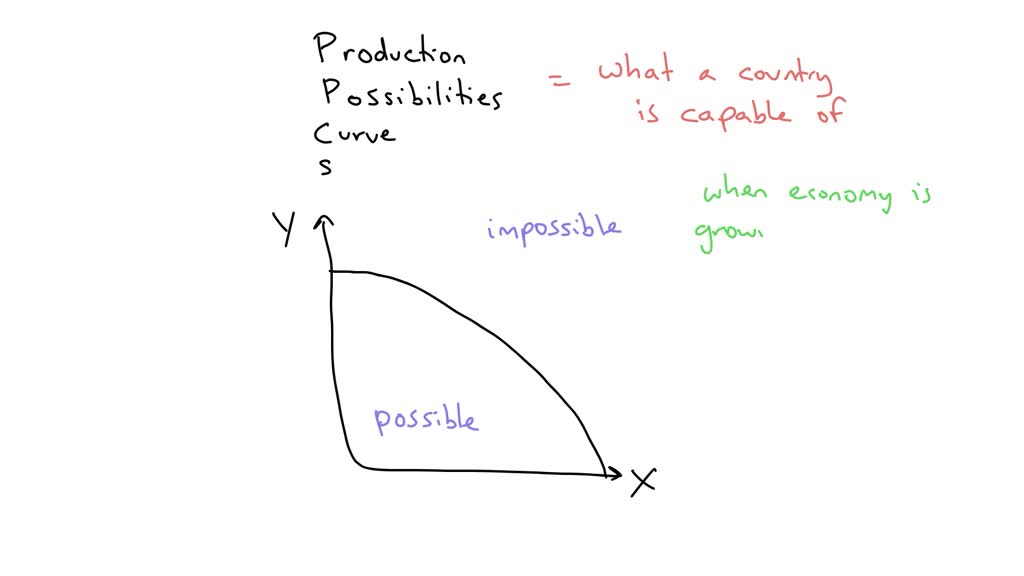
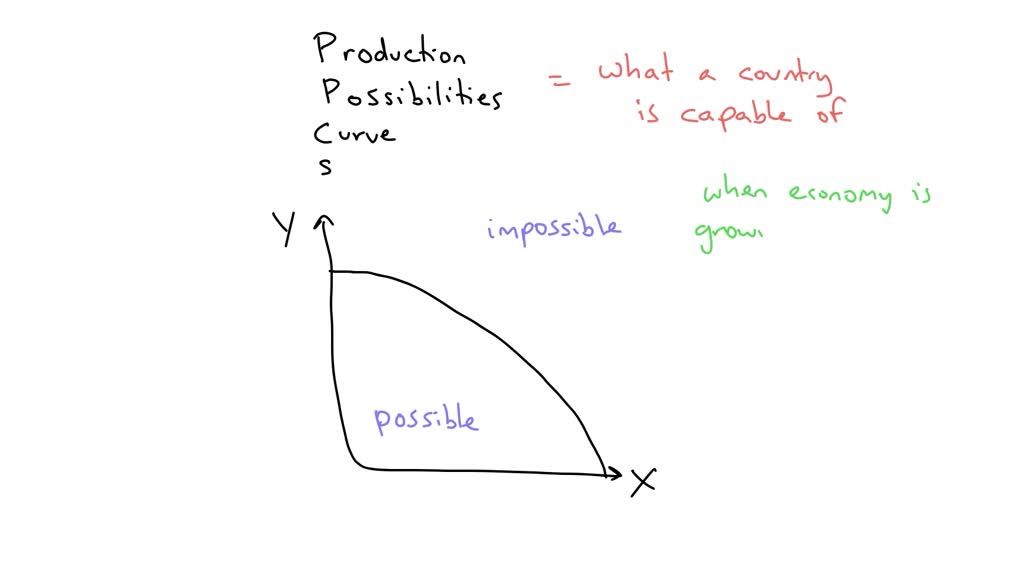
Understanding the Production Possibility Curve (Ppc)
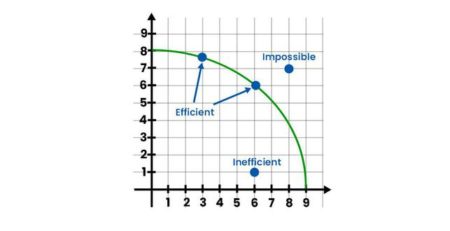
The Production Possibility Curve (Ppc) is a graphical representation of the maximum combinations of goods and services that an economy can produce given its resources and technology. By increasing output, an economy can shift its Ppc outward, reflecting its increased productive capacity and potential for economic growth.
When an economy operates within the bounds of its Ppc, it is said to be operating at full employment and maximizing its available resources efficiently. However, when output increases and the Ppc expands, the economy can produce more goods and services without sacrificing the production of other goods and services. This increase in output signifies economic growth and opens up new opportunities.
The Factors Driving Output Expansion
The expansion of output and the subsequent increase in the Ppc is influenced by various factors. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key drivers:
1. Technological Advancements:
Technological advancements play a crucial role in driving output growth. Through innovation and the adoption of new technologies, economies can enhance their productive capacity, improve efficiencies, and produce more with the same or fewer resources. Technological progress fuels economic growth, as it allows for the creation of new industries, products, and services.
2. Investment in Capital:
Investment in capital, such as machinery, equipment, and infrastructure, is vital for increasing output. By expanding and upgrading their capital stock, economies can boost productivity, automate processes, and enhance their overall production capabilities. Increased capital investment leads to higher output levels and paves the way for economic expansion.
3. Human Capital Development:
The knowledge, skills, and abilities of a workforce contribute significantly to output growth. Investing in education, training, and skill development programs fosters human capital development, empowering individuals to contribute more effectively to the economy. A highly skilled and productive workforce translates into increased output, innovation, and competitiveness.
The Implications of Increased Output and Economic Growth
The implications of increased output and economic growth are wide-ranging and influential. Let’s explore some of the key implications:
1. Improved Living Standards:
Higher output levels and economic growth lead to improved living standards for individuals within an economy. Increased production of goods and services means that people have access to more opportunities, better quality products, and a higher standard of living. Economic growth can result in reduced poverty levels and increased prosperity for a nation’s citizens.
2. Job Creation and Reduced Unemployment:
When output increases, new jobs are created to meet the growing demand for goods and services. Economic growth stimulates employment opportunities and reduces unemployment rates. This, in turn, fuels consumer spending, further driving economic expansion and creating a positive cycle of growth.
3. Increased Investment and Innovation:
As output expands and the economy experiences growth, it attracts increased investment from both domestic and foreign sources. The prospect of a larger market and higher returns on investment encourages entrepreneurs and businesses to innovate, develop new products, and explore emerging industries. This dynamism strengthens the economy and fosters long-term sustainability.
Key Takeaways: When Output Increases the Ppc of the Economy?
2. An increase in output means the economy is capable of producing more goods and services.
3. This implies that the economy can now consume more and improve the standard of living.
4. Factors such as technological advancements or increased resources can lead to an increase in output.
5. The increase in PPC signifies the potential for greater economic prosperity and opportunities for development.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our Frequently Asked Questions section where we address common queries regarding the impact of increased output on the PPC (Production Possibility Curve) of an economy. Find answers to your questions below to gain a better understanding of how changes in output affect an economy’s PPC.
1. How does an increase in output affect the PPC of an economy?
When output increases, it has a positive impact on the PPC of an economy. An increase in output means that the economy is capable of producing more goods and services within a given time period. This leads to an outward shift of the PPC curve, indicating that the economy’s production potential has expanded. As a result, the economy can now produce more of one good without sacrificing the production of another good.
This increase in output is often achieved through advancements in technology, increased investments in capital, and improvements in the efficiency of production processes. By increasing output, an economy can experience economic growth and improve the living standards of its population.
2. How does an increase in output affect resource allocation?
When output increases, resource allocation within an economy undergoes changes. As the economy produces more goods and services, it requires a greater amount of resources such as labor, capital, and raw materials. This increased demand for resources can lead to changes in their allocation.
In a situation where an economy experiences an increase in output, the allocation of resources may shift towards sectors or industries that are experiencing higher demand. The resources will be redirected to these sectors to support increased production levels, ensuring that the economy can meet the growing demand for goods and services. This reallocation of resources plays a crucial role in facilitating economic growth and development.
3. Can an increase in output lead to inflation?
In some cases, an increase in output can lead to inflation, but it is not always the case. Inflation occurs when there is an increase in the general level of prices in an economy. When output increases, the demand for goods and services can also increase. If the increase in demand outpaces the increase in supply, it can lead to upward pressure on prices, resulting in inflation.
However, it’s important to note that other factors such as the availability of resources, productivity, and the overall state of the economy can influence the relationship between output and inflation. Additionally, an increase in output can also lead to improvements in productivity, which can help offset inflationary pressures. Overall, the relationship between output and inflation is complex and depends on various factors.
4. How does an increase in output affect employment?
An increase in output can have a positive impact on employment within an economy. When output increases, there is a greater demand for labor to support the increased production levels. This can lead to job creation and reduce unemployment rates.
However, the exact impact on employment will depend on various factors, including the labor market conditions, the skill requirements of the industries experiencing increased output, and the availability of labor. It’s important to note that technological advancements can also influence employment levels, as they can replace certain jobs with automated systems. Nonetheless, in general, an increase in output tends to have a positive correlation with employment.
5. How does an increase in output affect the standard of living?
An increase in output can positively impact the standard of living within an economy. When the economy produces more goods and services, it can provide its population with a greater variety and quantity of products, resulting in an improved standard of living.
Increased output often leads to higher incomes, job creation, and improved access to goods and services. This can enhance people’s quality of life by providing them with more options and opportunities for consumption. Additionally, an increase in output can also lead to technological advancements, which can further boost the standard of living through innovations and improvements in various aspects of life.
PPCs for increasing, decreasing and constant opportunity cost | AP Macroeconomics | Khan Academy
Summary
When the output of an economy increases, it means that more goods and services are being produced. This has a positive effect on the PPC (Production Possibility Curve) of the economy. The PPC shows the different combinations of two goods that an economy can produce given its resources and technology. When output increases, the economy can produce more of both goods, moving the PPC outward.
Increasing output leads to economic growth and improved living standards. It allows for more goods and services to be available for people to consume. This can result in higher incomes, better infrastructure, and improved access to education and healthcare. However, increasing output also requires utilizing resources efficiently and investing in technological advancements. Without these efforts, the economy may face constraints that limit its ability to increase output and experience economic growth. Therefore, it is important for policymakers and businesses to focus on strategies that promote productivity and innovation to ensure sustained economic progress.







Leave a Reply